What is the HVAC Systems in Singapore

Definition of HVAC
HVAC, which stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, refers to the technology and systems used to control and regulate indoor environmental conditions.
In Singapore, where extreme heat and humidity are common, HVAC systems are essential for creating comfortable living and working spaces.
These systems are designed to maintain desired temperature, humidity, and air quality levels, providing a pleasant and healthy indoor environment.

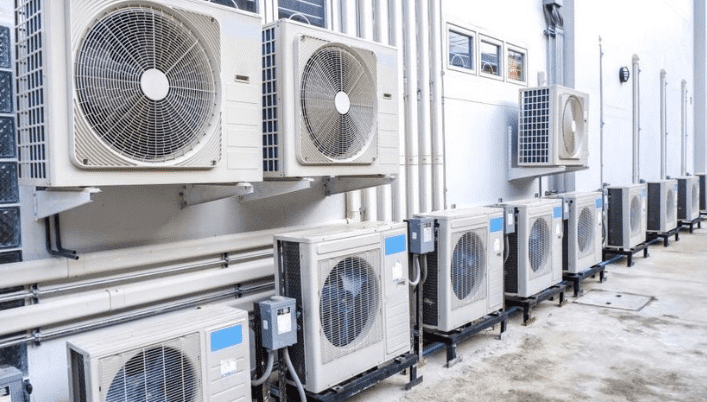
Benefits of HVAC in Singapore
Heat and Cool
The primary function of HVAC systems is to provide heating and cooling capabilities.
In Singapore’s tropical climate, where temperatures can rise to uncomfortable levels, having a reliable cooling system is essential for creating a comfortable living and working environment.
Energy Efficiency
Modern HVAC systems are designed to be energy-efficient, helping to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Many systems come with advanced features such as programmable thermostats, which allow users to set temperature schedules and optimize energy usage.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality.
HVAC systems include ventilation components that bring in fresh air from outside and filter out pollutants, allergens, and other contaminants, ensuring a healthy living or working environment.
Improved Air Quality
HVAC systems play a significant role in improving indoor air quality.
They help filter out dust, smoke, odors, and other pollutants, creating a cleaner and healthier environment for occupants.
Acceptable Indoor Air Quality
Singapore’s Building and Construction Authority (BCA) has set standards for acceptable indoor air quality in buildings.
HVAC systems help maintain these standards by ensuring proper air circulation, temperature, and humidity levels.
Heat Pump Systems
Heat pump systems are a particularly energy-efficient option for heating and cooling in Singapore.
They utilize the ambient heat from the environment and transfer it indoors during the colder months, reducing the reliance on heating oil or other energy sources.
Temperature Regulation
HVAC systems allow for precise temperature regulation, ensuring that indoor spaces remain comfortable even during extreme weather conditions.
This is particularly important in commercial buildings where occupants have different comfort preferences.
Energy Savings
Efficient HVAC systems can lead to significant energy savings for both residential and commercial buildings.
The use of energy-efficient equipment and proper system design can help reduce overall energy consumption and costs.
Key Features of HVAC Systems
Air Handler
The air handler is an essential component of HVAC systems.
It is responsible for circulating and distributing conditioned air throughout the building.
It contains the blower, heating or cooling elements, filters, and dampers.
Outdoor Unit
The outdoor unit of an HVAC system houses the compressor, condenser, and other components necessary for heat transfer.
It is responsible for expelling heat during the cooling process and absorbing heat during the heating process.
Control System
The control system of an HVAC system monitors and regulates the various components to maintain the desired indoor environmental conditions.
It can be programmed to adjust temperature, humidity, and other parameters automatically.
Air Distribution
Air distribution refers to the delivery of conditioned air to different areas or rooms within a building.
Proper air distribution ensures that every space receives adequate cooling, heating, and ventilation.
Ventilation System
The ventilation system in an HVAC system brings in fresh outdoor air and removes stale indoor air.
It includes components such as fans, air filters, and ductwork to facilitate the exchange of air while maintaining desired air quality levels.
Air Intake and Fresh Air Intake
The air intake is the area where the system draws in air for conditioning.
It is essential to have proper air intakes to ensure optimal system performance and avoid recirculating stale air.
Fresh air intake refers to the component that brings in outdoor air for ventilation purposes.
Mechanical Ventilation Systems
Mechanical ventilation systems are designed to provide controlled and continuous fresh air supply to indoor spaces.
They help remove pollutants, maintain acceptable indoor air quality, and comply with building regulations.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key feature of modern HVAC systems.
They utilize advanced technologies, such as variable speed motors and energy recovery systems, to minimize energy consumption and maximize performance.
Air flow and ASHRAE
Proper air flow is crucial for effective HVAC system operation.
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provides guidelines and standards for proper air flow design and maintenance.
Air Handling Unit
The air handling unit (AHU) is an integral part of HVAC systems.
It conditions the air by removing heat and humidity, filters out contaminants, and distributes the conditioned air to different parts of the building through a network of ducts.
HVAC systems in Singapore play a vital role in maintaining comfortable and healthy indoor environments.
They provide heating, cooling, and ventilation capabilities while ensuring energy efficiency and proper air quality.
Understanding the key features and benefits of HVAC systems can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions when it comes to creating a conducive living or working environment.
Key Takeaways
- Definition of HVAC: HVAC stands for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, essential for regulating indoor environmental conditions in Singapore’s hot and humid climate.
- Benefits of HVAC in Singapore:
- Provides heating and cooling capabilities for comfort.
- Energy-efficient designs reduce consumption and lower utility bills.
- Ensures proper ventilation for good indoor air quality.
- Filters out pollutants, improving overall air quality.
- Heat Pump Systems: Energy-efficient option utilizing ambient heat for heating and cooling.
- Temperature Regulation: HVAC allows precise temperature control, crucial for different comfort preferences in commercial buildings.
- Energy Savings: Efficient HVAC systems lead to significant energy savings in both residential and commercial buildings.
- Key Features of HVAC Systems:
- Air Handler: Circulates conditioned air.
- Outdoor Unit: Contains compressor and condenser.
- Control System: Monitors and regulates HVAC components.
- Air Distribution: Delivers conditioned air to different areas.
- Ventilation System: Brings in fresh air and removes stale air.
- Types of HVAC Systems:
- Split System, Ductless Mini-Split, District Heating, Central Air, Natural Ventilation, Energy-Efficient Systems.
- Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Considerations for cooling, heating, energy efficiency, air filtration, and outdoor units.
- How HVAC Systems Work:
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning functions explained.
- Importance of air filtration for indoor air quality.
- Ventilation in HVAC Systems:
- Effective ventilation crucial for air quality and comfort.
- Natural ventilation vs. mechanical ventilation compared.
- Role of Air Infiltration and Outdoor Air explained.
- Air Distribution in HVAC Systems:
- Proper air distribution essential for efficient HVAC operation.
- Flow of air, types of HVAC systems, and energy efficiency considerations.
- Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems:
- Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) for optimizing energy costs.
- Demand Controlled Ventilation (DCV) adapts ventilation rates based on occupancy.
- Natural ventilation and radiative cooling contribute to energy efficiency.
Types of HVAC Systems

Exploring Different Types of HVAC Systems
When it comes to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, there are several options available to meet the unique needs of different spaces.
Here are some of the most common types of HVAC systems:
- Split System: This is the most traditional type of HVAC system, commonly found in residential and small commercial buildings. It consists of two units – an indoor unit that contains the evaporator coil and an outdoor unit that houses the compressor and condenser coil.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: These systems are similar to split systems but do not require ductwork. They are ideal for heating or cooling individual rooms or areas and offer greater flexibility in terms of installation.
- District Heating: This system is commonly used in urban areas where a centralized heating plant distributes hot water or steam through a network of pipes to multiple buildings.
- Central Air: This is a popular choice for larger residential and commercial buildings. It uses a ductwork system to distribute conditioned air throughout the entire building.
- Natural Ventilation: This system relies on natural airflow through windows, doors, and other openings to provide cooling and fresh air. It is often used in buildings where energy efficiency and sustainability are priorities.
- Energy-Efficient Systems: The HVAC industry is continuously evolving to develop more energy-efficient systems. These systems incorporate advanced technologies and practices to minimize energy consumption and reduce environmental impact.
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provides guidelines and standards to ensure the design and installation of efficient HVAC systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various HVAC Systems
Each HVAC system has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Here are some considerations for different types of HVAC systems:
- Cooling and Heating: Some HVAC systems provide both cooling and heating capabilities, allowing for year-round comfort.
- Central Heating and Cooling System: Central HVAC systems offer convenience and uniform temperature control throughout the entire building. However, they require ductwork installation and can be costly.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient HVAC systems help save on utility bills and reduce carbon footprint. They utilize advanced technologies like variable-speed compressors and smart thermostats.
- Air Filtration: HVAC systems can incorporate air filtration systems to improve indoor air quality by removing pollutants and allergens from the air.
- Outdoor Units: Some HVAC systems have outdoor units that may take up valuable outdoor space or require proper shielding and maintenance.
When selecting an HVAC system, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of the space, energy efficiency goals, and budget constraints.
Consulting with a professional HVAC contractor will ensure the right system is chosen and installed correctly to provide optimal comfort and efficiency.
How HVAC Systems Work
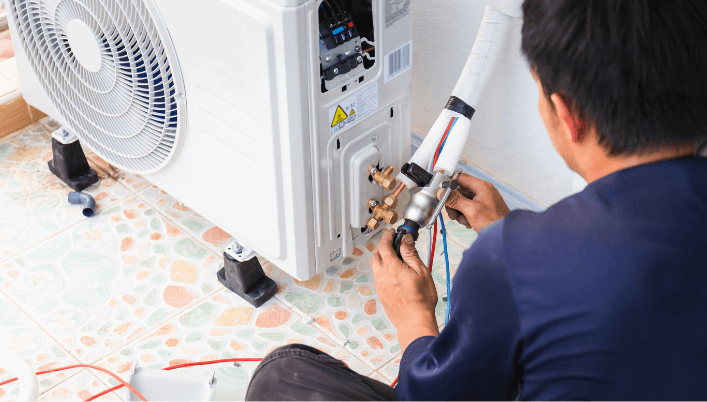
The Functioning of Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor environments by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality.
These systems work by moving air throughout a space, ensuring that it is properly conditioned.
Here is an overview of how HVAC systems function:
- Heating: Heating systems in HVAC utilize various sources, such as gas, electricity, or heat pumps, to warm the air. The heated air is then distributed throughout the space via ductwork or radiation systems, raising indoor temperatures to the desired level.
- Ventilation: Ventilation is essential for maintaining good air quality and removing stale air from the building. It involves bringing in fresh outside air and exhausting indoor air to the outside. Ventilation systems can be mechanically driven or rely on natural ventilation, such as windows or openings.
- Air Conditioning: Air conditioning units work by extracting heat and moisture from the air, thereby cooling and dehumidifying it. These units use refrigerants to facilitate the heat transfer process, allowing for the circulation of cool air throughout the space.
To achieve these functions, HVAC systems are equipped with components such as fans, blowers, compressors, and coils.
These work together to regulate the flow of air, control temperatures, and achieve the desired comfort levels.
Modern HVAC systems may also include energy-efficient features like variable-speed compressors and smart thermostats to optimize energy consumption.
Air conditioner plays a vital role in providing comfort and maintaining appropriate indoor air quality.
The use of air conditioning equipment, such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, has become prevalent in modern society.
These systems draw in air from the surrounding environment, filter it, and then release it into our homes and workplaces.
It is crucial to understand that not all types of air are the same.
The air outdoors can be polluted with dust, allergens, and other contaminants, while the air inside our homes can be stale and lack proper ventilation.
Air conditioning helps to address these issues by cooling the air and regulating its quality.
It filters out pollutants, controls humidity levels, and ensures a healthy and comfortable living environment.
By investing in modern air conditioning technology, we can purify and cool the air that surrounds us, enhancing our overall well-being and quality of life.
The Role of Air Filtration
Air filtration is an important aspect of HVAC systems as it helps improve indoor air quality.
Filtration systems remove pollutants, allergens, and particles from the air, ensuring that the circulated air is clean and healthy to breathe.
Here are some key points about air filtration in HVAC systems:
- Improve Indoor Air Quality: Air filters in HVAC systems trap dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles, preventing them from circulating in the indoor environment. This helps reduce allergies and respiratory issues associated with poor air quality.
- Acceptable Indoor Air Quality: HVAC systems are designed to maintain acceptable indoor air quality levels as defined by industry standards. This includes controlling the concentration of pollutants, temperature, humidity, and air circulation rates to ensure a comfortable and healthy environment.
- Ventilation Systems: Air filters are often integrated into ventilation systems to improve air quality further. These systems bring in fresh outdoor air and filter it before distributing it throughout the building.
- Demand Controlled Ventilation Systems: Some HVAC systems incorporate demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) systems, which adjust the amount of outside air brought in based on occupancy levels or other factors. This helps optimize energy consumption while maintaining air quality.
Air filtration systems and regular maintenance of filters are essential to ensure the effective operation of HVAC systems.
They help extend the lifespan of the equipment and prevent the build-up of dirt and debris that can hinder performance.
HVAC systems work by heating, ventilating, and conditioning the air to maintain comfortable indoor environments.
Air filtration plays a vital role in improving indoor air quality, ensuring that occupants breathe clean and healthy air.
Proper installation, maintenance, and regular filter replacement are important for the efficient operation of HVAC systems.
Ventilation in HVAC Systems
Importance of Effective Ventilation
Effective ventilation is a crucial aspect of HVAC systems as it plays a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality and creating a comfortable environment.
It involves the process of bringing in fresh outdoor air and removing stale air from the building.
Here are some key points about the importance of effective ventilation:
- Natural Ventilation: Natural ventilation utilizes natural forces such as wind and temperature differences to circulate air. It can be achieved through operable windows, vents, or other openings. Natural ventilation helps improve indoor air quality and reduce the reliance on mechanical ventilation systems, thus saving energy.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation systems, on the other hand, rely on fans or other mechanical devices to circulate and exchange air. They are essential in buildings where natural ventilation is insufficient or not possible. Mechanical ventilation helps remove pollutants, control humidity levels, and ensure a constant supply of fresh outdoor air for occupants.
- Adequate Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is necessary to maintain optimal indoor air quality and prevent the buildup of pollutants, allergens, and moisture. It helps reduce the risk of respiratory problems, allergies, and the spread of infectious diseases.
- Outdoor Air Quality: Effective ventilation ensures that the outdoor air being brought into the building is of good quality. Filters and air purifiers may be used to further enhance the air quality by removing contaminants and allergens.
- Air Infiltration and Ventilation Centre (AIVC): The Air Infiltration and Ventilation Centre is an organization that promotes knowledge and research on ventilation and air infiltration. It provides guidelines and best practices for effective ventilation strategies and technologies.
Natural Ventilation vs. Mechanical Ventilation
When it comes to ventilation methods, there are two main types: natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation.
Here’s a comparison between the two:
- Natural Ventilation: Natural ventilation relies on natural forces and airflow paths to provide ventilation. It can be achieved through strategically placed windows, vents, or other openings. Natural ventilation is energy-efficient and relies on the natural environment for air circulation. However, it may be limited by external factors such as weather conditions and noise pollution.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Mechanical ventilation systems use fans, blowers, or other mechanical devices to distribute and exchange air. These systems are controlled and can be designed to meet specific airflow requirements. Mechanical ventilation provides a more consistent and controlled air exchange, ensuring a steady supply of fresh outdoor air. It is suitable for buildings with limited or no access to natural ventilation.
Using a combination of natural and mechanical ventilation strategies can provide optimum results.
For example, opening windows to allow fresh air in during favorable weather conditions can complement mechanical ventilation systems, reducing energy consumption while maintaining indoor air quality.
Effective ventilation is essential in HVAC systems to maintain indoor air quality and create a comfortable environment.
Understanding the importance of adequate ventilation and the differences between natural and mechanical ventilation can help ensure the optimal functioning of HVAC systems.
By considering the specific needs of the building and utilizing appropriate ventilation strategies, businesses can achieve a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
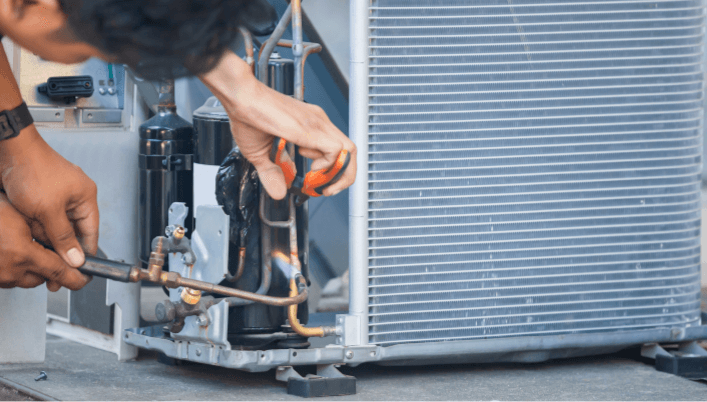
HVAC Equipment and Components

Essential Equipment in HVAC Systems
When it comes to HVAC systems, there are several essential components and equipment that contribute to their overall functionality.
Here are some key elements commonly found in HVAC systems:
- HVAC Stand: The HVAC stand is a platform or base on which the HVAC equipment is installed. It provides stability and support for the various components of the system.
- Air Handling Unit: The air handling unit (AHU) is responsible for circulating and conditioning the air within the system. It includes components such as fans, filters, dampers, and coils to regulate airflow, temperature, and humidity.
- Heating and Air Conditioning Systems: These systems are the main components of HVAC systems. Heating systems can include furnaces, boilers, or heat pumps, while air conditioning systems usually consist of compressors, condensers, and evaporators.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ductless mini-split systems are an alternative to traditional ducted HVAC systems. They consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units, which are connected by refrigerant lines. These systems are ideal for situations where ductwork is not feasible or desired.
- Unit: The unit refers to the HVAC equipment collectively. It includes the heating and cooling components, as well as any associated ductwork.
- Pressure: Pressure is an important factor in HVAC systems. Fans, compressors, and other components rely on pressure differentials to move air or refrigerant throughout the system.
- Fan Coil Units: Fan coil units are used for localized heating and cooling. They consist of a coil, a fan, and a control unit and are commonly found in hotels, apartments, and office buildings.
- Heating Oil: Heating oil is a common fuel source for heating systems in certain regions. It is typically used in oil furnaces or boilers.
- Outdoor Temperatures: Outdoor temperatures play a crucial role in the operation of HVAC systems. They determine the heat transfer rates and affect the efficiency of heating and cooling processes.
Understanding the Role of Air Intake and Outdoor Air
Air intake and outdoor air are essential aspects of HVAC systems. Here’s why they are important:
- Air Intake: Air intake refers to the process of bringing fresh air from outside into the HVAC system. It is necessary to maintain proper ventilation, air quality, and temperature control within indoor spaces. Outdoor air intakes are strategically located to ensure the supply of clean, fresh air.
- Outdoor Air: Outdoor air provides the necessary oxygen for combustion in heating systems and dilutes indoor pollutants. It helps maintain a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
- Fresh Air from Outside: Fresh outdoor air is beneficial for occupants’ well-being, as it reduces the concentration of indoor pollutants, allergens, and odors.
- Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV): HRV systems recover heat from exhaust air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air. This helps improve energy efficiency by reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
- Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV): ERV systems, similar to HRV systems, recover both heat and moisture from the exhaust air. This helps maintain indoor humidity levels and improve energy efficiency.
- Outdoor Air Intakes: Outdoor air intakes are openings in the building envelope or dedicated ducts that allow the entry of outdoor air into the HVAC system.
- Air Leakage: Proper sealing and insulation of the building envelope is crucial to prevent unwanted air leakage, which can affect the effectiveness of the HVAC system.
- Flow of Refrigerant: In air conditioning systems, the flow of refrigerant is responsible for removing heat from indoor spaces and transferring it outdoors.
Understanding the role of air intake and the importance of outdoor air in HVAC systems is crucial for maintaining optimal indoor air quality and ensuring the efficient operation of the system.
By considering these factors, businesses can create a comfortable and healthy environment for their occupants
Air Distribution in HVAC Systems
The Significance of Proper Air Distribution
Proper air distribution is a crucial aspect of HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.
It ensures that the conditioned air is delivered efficiently and effectively to different spaces within a building.
Here’s why proper air distribution is so significant:
- Air Handling: In HVAC systems, the air handling unit (AHU) plays a vital role in circulating and conditioning the air. It includes components such as fans, filters, dampers, and coils, which regulate airflow, temperature, and humidity. Proper air distribution ensures that the conditioned air is distributed evenly throughout the building, maintaining a comfortable environment.
- Flow of Air: The flow of air within an HVAC system is essential for maintaining proper ventilation and temperature control. Proper air distribution ensures that the air is directed to the areas where it is needed the most, reducing energy waste and improving overall system efficiency.
- Types of HVAC Systems: Different types of HVAC systems rely on proper air distribution to function effectively. For example, in central systems, ductwork is used to distribute the conditioned air throughout the building. In ductless mini-split systems, air handlers are installed in individual rooms or zones, providing localized air distribution.
- Efficiency and Comfort: Proper air distribution helps maintain a comfortable indoor environment by ensuring that conditioned air reaches all areas evenly. This eliminates hot or cold spots and prevents issues such as poor air quality and humidity imbalance.
- Natural Ventilation: In addition to mechanical systems, natural ventilation can also contribute to proper air distribution. It involves the use of windows, vents, and other openings to facilitate the flow of fresh air into the building. By incorporating natural ventilation strategies, businesses can enhance indoor air quality and reduce energy consumption.
- ASHRAE Transactions: The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) publishes studies and research papers on air distribution and its impact on HVAC systems. These resources provide valuable insights into best practices for achieving optimal air distribution.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper air distribution is crucial for optimizing energy efficiency in HVAC systems. By ensuring that conditioned air is delivered efficiently to different spaces, businesses can reduce energy waste and lower operating costs.
Proper air distribution is essential for the efficient and effective operation of HVAC systems.
It ensures that conditioned air is distributed evenly throughout the building, maintaining a comfortable indoor environment and optimizing energy efficiency.
By considering the significance of proper air distribution, businesses can create a healthier and more energy-efficient environment for their occupants.
Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems | Energy Recovery Ventilation
Energy Recovery Ventilation
Energy recovery ventilation (ERV) is a crucial component of modern HVAC systems.
It helps to optimize energy costs and improve the efficiency of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
ERV involves the exchange of heat and moisture between the indoor and outdoor air streams, allowing for the recovery of energy that would otherwise be lost during ventilation.
By incorporating ERV into HVAC systems, businesses can reduce their cooling and heating power requirements, resulting in lower energy costs.
This technology enables the pre-conditioning of outdoor air with the exhaust air, minimizing the need for additional cooling or heating.
ERV systems also play a vital role in maintaining proper indoor air quality by effectively filtering and purifying the incoming air.
Demand Controlled Ventilation Systems
Demand Controlled Ventilation (DCV) systems are another energy-efficient solution for HVAC systems.
These systems monitor the occupancy and air quality in different spaces and adjust the ventilation rates accordingly.
By adapting the supply air to match the actual demand, DCV systems can significantly reduce energy consumption.
DCV systems utilize sensors and control strategies to optimize the amount of outdoor air brought into the building while maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
These systems are particularly beneficial in spaces with varying occupancy levels, such as conference rooms or classrooms.
By providing appropriate ventilation only when needed, DCV systems help businesses save on energy costs without compromising air quality.
Natural Ventilation and Radiative Cooling
In addition to mechanical systems, natural ventilation plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency in HVAC systems.
Natural ventilation involves the strategic use of windows, vents, and other openings to facilitate the flow of fresh outdoor air into the building.
By incorporating natural ventilation strategies, businesses can reduce their reliance on mechanical ventilation and decrease energy consumption.
Furthermore, recent developments in the field of radiative cooling have provided innovative solutions to enhance energy efficiency in HVAC systems.
Radiative cooling technologies utilize specialized materials to cool down the surrounding air without the need for energy-intensive processes.
By harnessing the cooling power of the night sky or the earth’s surface, these systems can significantly reduce energy consumption for cooling purposes.
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of HVAC systems.
Incorporating technologies like energy recovery ventilation, demand-controlled ventilation systems, and natural ventilation can help businesses optimize their energy costs and create a healthier and more sustainable indoor environment.
By adopting these strategies, businesses can improve the efficiency of their HVAC systems and contribute to overall energy conservation efforts.
Exhaust Air and Air Conditioning
The Relationship between Exhaust Air and HVAC Systems
To understand the relationship between exhaust air and HVAC systems, it is important to delve into the concept of proper ventilation.
HVAC systems, which stand for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, play a crucial role in maintaining good indoor air quality and creating a comfortable living space.
Ventilation is an integral part of HVAC systems as it involves the exchange of stale air with fresh outdoor air, ensuring a healthy and pleasant environment inside buildings.
One key component of ventilation is the management of exhaust air.
When HVAC systems are in operation, they not only provide conditioned air but also remove the stale air from the building.
This process ensures that contaminants, such as odors, humidity, and pollutants, are expelled, maintaining good indoor air quality.
Exhaust air is typically expelled using exhaust fans or systems that create pressure differences to facilitate its flow.
These systems work in coordination with the air conditioning units to maintain the desired temperature and humidity levels inside the building.
By removing exhaust air, HVAC systems ensure that the air being circulated is fresh and free from contaminants.
Proper ventilation effectiveness can be achieved by balancing the intake of fresh outdoor air with the exhaust air.
This balance is crucial to maintain energy efficiency and prevent an excessive exchange of air that could lead to unnecessary cooling or heating requirements.
HVAC systems are designed to optimize this balance, ensuring adequate air filtration and circulation.
The management of exhaust air also contributes to energy recovery ventilation, a technology that optimizes energy costs.
Energy recovery ventilation involves the exchange of heat and moisture between the incoming and outgoing air streams.
By recovering energy that would otherwise be lost during ventilation, HVAC systems can reduce cooling and heating power requirements, resulting in lower energy consumption and costs.
Another aspect to consider is the integration of natural ventilation alongside mechanical systems.
Natural ventilation utilizes windows, vents, and other openings to facilitate the flow of fresh outdoor air into the building.
By incorporating natural ventilation strategies, HVAC systems can reduce the reliance on mechanical ventilation and decrease energy consumption.
The relationship between exhaust air and HVAC systems is synonymous with the overall ventilation effectiveness and indoor air quality.
Proper management of exhaust air ensures the removal of stale air, while fresh outdoor air is brought in, minimizing energy consumption and maintaining a comfortable and healthy environment for occupants.
By considering technologies like energy recovery ventilation and the integration of natural ventilation, businesses can optimize their HVAC systems and contribute to energy conservation efforts while enjoying the benefits of improved indoor air quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
These systems, which encompass heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, are responsible for regulating the temperature, humidity, and air quality in buildings.
HVAC technicians are trained professionals who ensure the proper installation, maintenance, and repair of these systems.
Understanding the Role of HVAC Systems
HVAC systems are designed to control the temperature and airflow within a building.
They are responsible for heating the air in colder months, cooling it during hot summers, and ensuring a constant supply of fresh, filtered air.
These systems include various components such as furnaces, boilers, air conditioners, heat pumps, and ventilation systems that work together to provide optimal comfort.
When it comes to heating, HVAC systems use different methods depending on the heating source.
For example, furnaces and boilers utilize gas or oil to generate heat, while heat pumps extract heat from the air or ground.
These systems can distribute warm air through ductwork or radiators, ensuring even heat distribution throughout the space.
Ventilation is another critical aspect of HVAC systems.
It involves the exchange of indoor and outdoor air to maintain good indoor air quality.
Ventilation systems can remove pollutants and odors from the air and control humidity levels.
They also help regulate the amount of fresh air being supplied to the space, ensuring a healthy and comfortable environment.
The Importance of Proper Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
Proper HVAC is essential for a variety of reasons.
Firstly, it provides thermal comfort by ensuring that the air temperature is within a comfortable range throughout the year.
This is particularly important in extreme climates where temperatures can be extremely cold or hot.
Additionally, HVAC systems help maintain indoor air quality by filtering out pollutants, allergens, and contaminants.
They also control humidity levels, which can prevent the growth of mold and mildew and reduce the risk of respiratory issues.
Energy efficiency is another significant aspect of HVAC systems.
Properly designed and maintained systems can help reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills.
High-efficiency HVAC equipment, such as ENERGY STAR certified systems, can provide even greater energy savings and environmental benefits.
Lastly, HVAC systems contribute to the overall well-being and productivity of building occupants.
A comfortable indoor environment promotes a sense of well-being and enhances productivity in both residential and commercial settings.
It also plays a crucial role in industries that require specific temperature and humidity control, such as healthcare facilities, data centers, and manufacturing plants.
Proper heating, ventilation, and air conditioning are essential for creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, investing in a well-designed HVAC system and regularly maintaining it ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and improved indoor air quality.
With the help of skilled HVAC technicians and quality equipment, you can enjoy year-round comfort and peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of ventilation and air conditioning in HVAC?
Ventilation and air conditioning are essential components of HVAC systems that help regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality in indoor spaces.
What is air filtration in HVAC?
Air filtration is the process of removing dirt, dust, allergens, and other particles from the air in HVAC systems, ensuring cleaner and healthier indoor air.
How are HVAC and air conditioning related?
HVAC encompasses heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, where air conditioning refers specifically to the cooling aspect of HVAC.
What is natural ventilation?
Natural ventilation is the process of using outside air to cool or ventilate indoor spaces without the use of mechanical systems.
What is an HVAC stand?
An HVAC stand is a platform or structure typically used to elevate HVAC equipment, such as outdoor condenser units, for better performance and protection.
What is outdoor air in HVAC?
Outdoor air in HVAC refers to fresh air brought into a building from the outside, usually through ventilation systems, to improve indoor air quality.
What is recovery ventilation in HVAC?
Recovery ventilation is a process in HVAC systems where heat or energy from exhaust air is transferred to incoming air, improving overall energy efficiency.
What is air intake in HVAC?
Air intake in HVAC refers to the process of drawing in outside air to provide necessary air supply for heating, cooling, and ventilation systems.
How does heating ventilation and air conditioning work?
Heating ventilation and air conditioning systems work by using various components, such as furnaces, air conditioners, and fans, to heat, cool, and circulate air within a building.












