Introduction to LRT in Singapore
Singapore’s Light Rail Transit (LRT) system is integral to the city-state’s efficient and comprehensive public transportation network.
The LRT provides convenient and reliable transportation options for residents and visitors, connecting various neighborhoods and key destinations.
Overview of the Light Rail Transit System in Singapore
The LRT system in Singapore consists of several lines, with the Bukit Panjang LRT being one of the most prominent ones.
The LRT lines are seamlessly integrated with the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system, allowing passengers to transfer quickly between the two modes of transportation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TuXIl_GDSZc
The LRT offers a comfortable and efficient way to travel short distances within neighborhoods, providing a convenient alternative to buses or private vehicles.
With its elevated tracks, the LRT provides passengers with scenic views of the surrounding areas as they travel.
History and development of LRT in Singapore
The development of the LRT system in Singapore began in the 1990s as part of the government’s efforts to enhance public transportation infrastructure.
The Bukit Panjang LRT line was first introduced, opening in 1999.
Over the years, the LRT system has expanded, adding additional lines to serve more areas.
The Land Transport Authority (LTA) has been responsible for planning, building, and maintaining the LRT system, ensuring its reliability and efficiency.
The introduction of the LRT has dramatically improved neighborhood connectivity, making it easier for residents to access amenities such as shopping malls, schools, and recreational facilities.
It has also contributed to reducing traffic congestion and promoting sustainable transportation options.
In conclusion, Singapore’s Light Rail Transit system provides efficient and convenient transportation options for residents and visitors.
With its seamless integration with the MRT system and continuous expansion, the LRT continues to enhance connectivity and accessibility across the city-state.
Key Takeaways
- Integral Transportation Network: Singapore’s Light Rail Transit (LRT) system is an essential part of the city’s public transportation network, providing convenient options for both residents and visitors.
- Seamless Integration: The LRT system is seamlessly integrated with the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system, allowing easy transfers between the two modes of transportation.
- Neighborhood Connectivity: LRT offers efficient travel within neighborhoods, offering a comfortable alternative to buses or private vehicles.
- Elevated Tracks: With elevated tracks, LRT passengers enjoy scenic views of surrounding areas during their journeys.
- Historical Development: The LRT system’s development started in the 1990s to enhance public transportation infrastructure, with the Bukit Panjang LRT as the first line.
- Continued Expansion: The LRT system has expanded over the years, with new lines added to serve more areas, improving connectivity and accessibility.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: LRT contributes to reducing traffic congestion and promoting sustainable transportation options in the city.
- Government Oversight: The Land Transport Authority (LTA) is responsible for planning, building, and maintaining the LRT system to ensure reliability and efficiency.
- Enhanced Neighborhood Access: LRT improves access to amenities such as shopping malls, schools, and recreational facilities within neighborhoods.
- Overall Impact: The LRT system in Singapore enhances connectivity, reduces traffic congestion, and provides efficient transportation options for residents and visitors.
LRT Lines in Singapore

Overview of the different LRT lines in Singapore
Singapore boasts an efficient and comprehensive public transportation system, which includes the Light Rail Transit (LRT) lines.
The LRT system in Singapore consists of two main lines: the Punggol LRT and the Bukit Panjang LRT.
The Punggol LRT is part of the more considerable Punggol New Town development and serves as a convenient mode of transport for residents.
It connects to the North East Line at Punggol MRT station, providing seamless transfers for commuters.
On the other hand, the Bukit Panjang LRT serves the Bukit Panjang area and connects to the Downtown Line at Bukit Panjang MRT station.
This line provides easy access to amenities and residential areas in Bukit Panjang and Choa Chu Kang.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWs3pAT0z0I
Description of each LRT line and its routes
The Punggol LRT consists of two loops: the Punggol East Loop and the Punggol West Loop.
The East Loop has seven stations, while the West Loop has six.
This line serves the Punggol residential estate, connecting it to key areas such as Sengkang and Punggol MRT stations.
The Bukit Panjang LRT runs along a single loop with 14 stations.
It serves the Bukit Panjang and Choa Chu Kang areas, providing convenient access to shopping malls, schools, and residential estates.
This line also connects to the Downtown Line at Bukit Panjang MRT station.
Different transport operators operate both LRT lines.
SBS Transit manages the Punggol LRT, while the Bukit Panjang LRT is operated by SMRT Trains.
These LRT lines complement the existing MRT network, making it easier for commuters to travel within Singapore.
In conclusion, the LRT lines in Singapore, namely the Punggol LRT and the Bukit Panjang LRT, play a crucial role in enhancing connectivity and accessibility for residents in these areas.
With seamless transfers to the MRT system, these LRT lines provide a convenient and efficient mode of transportation for Singaporeans and visitors alike.
Benefits of LRT in Singapore

Advantages of using the LRT system in Singapore
The LRT system in Singapore has several advantages that make it a preferred mode of transportation for commuters.
Here are some of the key benefits:
- Efficient and convenient: The LRT system provides a rapid transit option that is reliable and efficient. With strategically located LRT stations, it offers easy access to various parts of the city, connecting seamlessly with the MRT lines and other modes of public transport.
- Reduced traffic congestion: By providing an alternative mode of transportation, the LRT system helps alleviate traffic congestion on the roads. Commuters can leave their cars at home and opt for the LRT, reducing the number of vehicles on the road and easing traffic flow.
- Environmental sustainability: The LRT system is an eco-friendly mode of transportation. It runs on electricity, reducing carbon emissions and creating a cleaner environment. By encouraging more people to use public transport, the LRT system helps reduce air pollution and promote sustainability.
- Improved connectivity: The LRT system expands the rail network in Singapore, enhancing connectivity between different neighborhoods and improving accessibility for residents. It provides a seamless connection to residential areas, commercial hubs, and educational institutions, making it easier for people to travel within the city.
- Enhanced passenger service: The LRT system offers comfortable and reliable passenger service. Commuters can enjoy a smooth and pleasant journey with well-maintained trains and stations. The system is designed to cater to the needs of passengers, ensuring their safety and convenience.
The impact of the LRT system on traffic congestion and environmental sustainability cannot be overstated.
Providing an efficient and eco-friendly mode of transportation contributes to the overall goal of creating a world-class transport system in Singapore.
Feasibility studies for expanding the LRT system, such as the Bukit Panjang Light Rail Transit (LRT), further demonstrate the commitment to improving public transport and exploring the feasibility of using LRT in different parts of the city.
Overall, the LRT system in Singapore offers numerous benefits, including improved connectivity, reduced traffic congestion, and environmental sustainability.
It is crucial in providing efficient and reliable public transport options for residents and visitors alike.
LRT Stations and Facilities

Description of the various LRT stations in Singapore
Singapore’s LRT (Light Rail Transit) system consists of several stations that provide convenient transportation options for residents and visitors.
The LRT stations are strategically located in different parts of the city, ensuring easy access to various neighborhoods.
The LRT service operates in two main areas: Bukit Panjang and Choa Chu Kang and Bukit Panjang and Buona Vista.
These stations serve as important transit points for commuters traveling within these regions.
Each LRT station is designed with the comfort and convenience of passengers in mind.
The stations have modern facilities such as ticketing machines, escalators, and elevators to ensure smooth and hassle-free journeys.
Additionally, there are clear signages and information boards to guide commuters.
Facilities and amenities available at the stations
In addition to the basic facilities, the LRT stations in Singapore offer a range of amenities to enhance the commuting experience.
These include comfortable seating areas, restrooms, and retail outlets where passengers can purchase snacks or other necessities.
The control center for the LRT system is located at the Bukit Panjang station.
From here, operators monitor the operations of the entire rail system and ensure its smooth functioning.
In any disruptions or emergencies, an operations control center coordinates response efforts.
To further improve connectivity, shuttle bus services are available at certain LRT stations.
These buses provide seamless transfers between different modes of transportation, such as MRT lines or other bus routes.
Overall, Singapore’s LRT system offers a reliable and efficient means of transportation for commuters.
With well-designed stations and various facilities and amenities, passengers can enjoy a comfortable journey while exploring different parts of the city.
Please note that this article is based on information available at the time of writing and may be subject to change.
LRT Fares and Ticketing

Information on fares and ticketing options for the LRT system
Singapore’s LRT (Light Rail Transit) system offers commuters convenient and affordable transportation options.
Regarding fares and ticketing, there are a few essential things to know.
The fare structure for the LRT system is distance-based, meaning that the further you travel, the higher the fare.
The fares range from $0.
77 to $1.
49, depending on the distance traveled.
You can use an EZ-Link or contactless bank card with a Mastercard or Visa logo to pay for your LRT ride.
There are several ticketing options available for LRT commuters.
The most popular choice is the EZ-Link card, a reloadable smart card that can be used for LRT rides and other public transportation modes in Singapore.
You can purchase an EZ-Link card at any TransitLink Ticket Office or General Ticketing Machines at MRT stations.
For occasional travelers or tourists, there is also the option of purchasing a Standard Ticket.
These single-use tickets are available at LRT stations and can be used for a one-way trip on the LRT system.
Types of tickets and payment methods available
In addition to the EZ-Link card and Standard Tickets, other payment methods are available for LRT rides.
Commuters can use their contactless bank cards with Mastercard or Visa logo to tap in and out of the LRT system.
To ensure smooth operations and assist commuters, each LRT station has an Operations Control Centre where staff members can answer questions or provide guidance on ticketing options.
The LRT system in Singapore currently operates in two areas: Bukit Panjang and Choa Chu Kang.
Each room has several LRT stations, providing convenient access to residential areas, shopping malls, and other amenities.
Overall, the LRT system in Singapore offers a reliable and efficient mode of transportation.
With various ticketing options available, commuters can choose the most suitable payment method.
So whether you’re a daily commuter or a tourist exploring the city, the LRT system is convenient for getting around Singapore.
LRT Operating Hours and Frequency
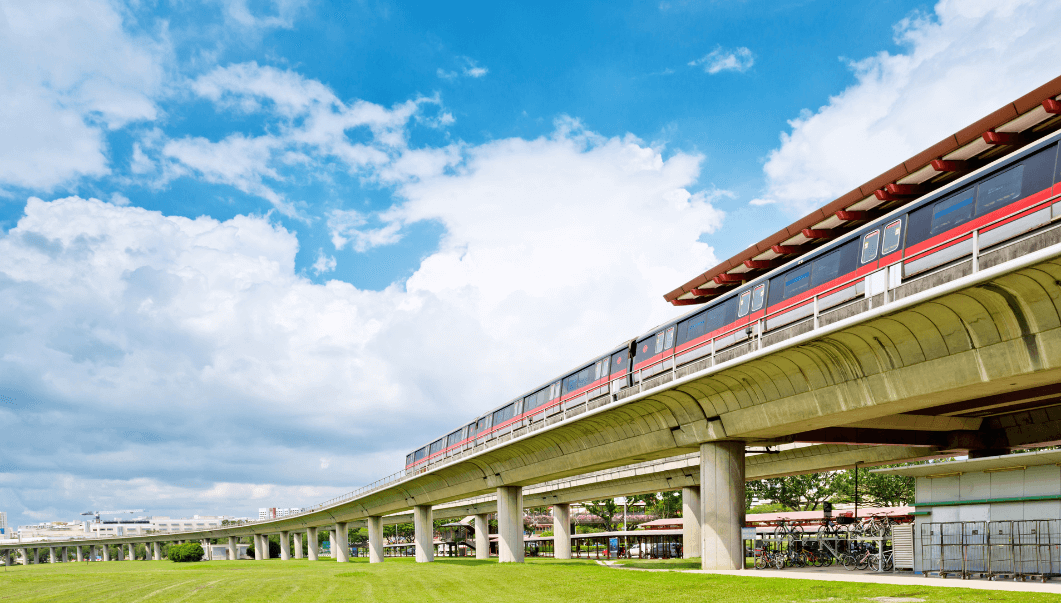

Details on the operating hours and frequency of LRT services
Singapore’s Light Rail Transit (LRT) system provides convenient transportation options for residents and visitors.
The operating hours and frequency of LRT services are designed to cater to the needs of commuters throughout the day.
The LRT services operate from early morning until late at night, ensuring that passengers can rely on this mode of transport for their daily commute.
The operating hours may vary slightly depending on the specific LRT system and station.
The frequency of LRT services is also carefully planned to ensure minimal waiting time for passengers.
During peak hours, trains run more frequently to accommodate the higher demand.
This ensures commuters can reach their destinations promptly, even during busy periods.
Peak and off-peak timings for each line
To further optimize the efficiency of the LRT system, peak and off-peak timings are implemented for each line.
Peak timings typically coincide with rush hour periods when more commuters travel.
During these times, trains run at shorter intervals to accommodate the increased passenger flow.
On the other hand, off-peak timings refer to periods with less demand for LRT services.
During these times, trains may run longer as fewer passengers travel.
Both peak and off-peak timings are carefully managed by SMRT Trains, the operator of the LRT system, in coordination with the Operations Control Centre.
This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, and commuters enjoy a smooth and reliable journey.
The LRT system operates in various areas of Singapore, including Bukit Panjang and Choa Chu Kang.
These areas benefit from the convenience and accessibility of the LRT services, connecting residents to other parts of the city seamlessly.
Overall, the operating hours and frequency of LRT services in Singapore are designed to meet the transportation needs of commuters, ensuring a reliable and efficient mode of travel throughout the day.
Safety and Security Measures

Overview of the safety and security measures implemented in the LRT system
The LRT system in Singapore prioritizes the safety and security of its commuters.
The Land Transport Authority (LTA) and SMRT have implemented various measures to ensure passengers’ secure and comfortable journeys.
To maintain safety, the LRT system has safety measures in place.
These include regular tracks, trains, and station inspections to identify potential hazards.
Emergency buttons are installed in all stations and trains, allowing passengers to alert authorities in case of emergencies quickly.
The Operations Control Centre monitors the entire rail system, ensuring prompt response to incidents or disruptions.
In terms of security, surveillance systems are installed throughout the LRT system.
These systems include CCTV cameras that monitor stations, platforms, and trains.
This helps deter criminal activities and provides evidence in case of any untoward incidents.
Emergency procedures and surveillance systems
The LTA and SMRT have established comprehensive emergency procedures to handle various situations.
In an emergency, such as a fire or medical emergency, trained staff members are deployed to provide immediate assistance.
The Operations Control Centre is crucial in coordinating emergency responses and communicating with relevant authorities.
Surveillance systems play a vital role in ensuring the safety and security of commuters.
The Operations Control Centre controls and monitors the signaling and train movements using advanced technology.
This allows for quick response to any abnormalities or disruptions in the system.
In recent years, there have been efforts to enhance safety measures further.
For example, after a review of train services, it was announced that LRT services would end an hour earlier to allow for more time for maintenance checks and repairs.
Overall, the safety and security measures implemented in the LRT system demonstrate Singapore’s commitment to providing a reliable and secure public transportation experience for its commuters.
Future Developments and Expansion Plans

Updates on upcoming developments and expansion plans for the LRT system in Singapore
Singapore’s LRT system has been integral to the city-state’s public transportation network, providing convenient and efficient travel options for commuters.
To meet the growing demand and improve connectivity, several future developments and expansion plans are in the pipeline.
New lines or extensions to existing lines
The Singapore Rapid Transit (SRT) network is set to expand with new lines and extensions to existing lines.
One of the upcoming developments is the extension of the Bukit Panjang LRT line, which will connect it to the upcoming Jurong Region Line.
This extension will enhance connectivity between the western and northern parts of Singapore.
In addition, there are plans to construct new LRT lines in areas with high population density and limited access to existing MRT stations.
These new lines will provide residents with more convenient travel options and reduce road congestion.
Transport Minister Khaw Boon Wan has emphasized expanding rail networks to meet future transportation needs.
The government aims to complete these developments within three years, demonstrating its commitment to improving public transportation infrastructure.
Feasibility studies have also been conducted for an LRT system in Punggol North.
If deemed viable, this project will further enhance connectivity in northeastern Singapore.
The expansion plans for the LRT system align with the government’s broader vision of creating a seamless and efficient public transportation network.
By expanding rail options, Singapore aims to provide commuters with faster, more reliable, and sustainable travel alternatives.
Summary
LRT in Singapore: A Brief Overview
Singapore’s Light Rail Transit (LRT) system has been integral to the city-state’s transportation network since its first line opened in 1999.
The LRT system consists of three networks, providing convenient and efficient transportation options for residents and visitors alike.
In recent news, the Bukit Panjang LRT line is set to close for two weekends in August temporarily.
This closure facilitates the installation of a new signaling system, which will enhance the reliability and efficiency of the LRT service.
The closure will occur early over two weekends to minimize commuter disruption.
The decision to upgrade the signaling system comes after a study conducted by the Land Transport Authority (LTA) in collaboration with the National University of Singapore and Singapore Polytechnic.
The study aimed to assess the feasibility of implementing an LRT system in the area and identified the need for improvements to meet the increased demand for transport services.
The Bukit Panjang LRT line serves 13 stations and is crucial in connecting neighboring towns.
It has been an essential mode of transport for residents and commuters, especially in anticipation of increased demand due to significant developments such as Suntec City.
To meet the growing transportation needs, plans are underway to introduce 19 new light rail vehicles and upgrade existing LRT stops.
These enhancements are part of Singapore’s goals for a world-class transport system that is efficient, reliable, and accessible.
SMRT Corporation operates the LRT system in Singapore in collaboration with the Land Transport Authority (LTA).
Both organizations are committed to providing safe and comfortable journeys for passengers while continuously improving the overall efficiency of the LRT network.
In conclusion, Singapore’s LRT system has significantly enhanced connectivity and accessibility within the city-state.
The upcoming upgrades and improvements, such as installing a new signaling system and introducing new light rail vehicles, demonstrate the commitment to meeting the increasing demand for transport services.
With continued efforts to provide a world-class transport system, the LRT in Singapore will continue to serve as a vital mode of transportation for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Sengkang LRT?
The Sengkang LRT is a light rail system in Singapore that serves the residential town of Sengkang.
It is part of the more extensive Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) network and provides an additional mode of public transportation for commuters.
What is a feeder service?
A feeder service is a public transportation service that “feeds” commuters from their homes to the main transportation hubs or interchange stations.
Public transport operators typically operate feeder services to provide convenient access to the leading rail services.
What is the Cross Island Line?
The Cross Island Line is a planned MRT line in Singapore connecting various parts of the island, including the East Coast and Changi Airport.
It will provide additional connectivity and enhance transportation options for residents and commuters.
What is the Circle Line?
The Circle Line is a fully underground MRT line in Singapore that forms a loop around the city center.
It connects with other MRT lines and provides convenient access to critical locations and attractions in the city.
What is the East West Line?
The East-West Line is one of Singapore’s oldest and busiest MRT lines.
It spans from the western part of the island to the eastern region, connecting major residential areas, commercial hubs, and critical transportation nodes.
What is the Thomson-East Coast Line?
The Property Price Index can be used in various ways.
The Thomson-East Coast Line is a new MRT line being constructed in Singapore.
It will run from the island’s northern part to the eastern region, improving connectivity and providing more transportation options for residents.
Who are the public transport operators in Singapore?
The public transport operators in Singapore include SMRT Corporation Ltd and SBS Transit.
They are responsible for operating and maintaining the MRT and LRT systems and bus services in the country.
What is the Singapore LRT?
The Singapore LRT, or the Light Rapid Transit, is a light rail system in Singapore.
It consists of several lines that serve different parts of the island, providing convenient and efficient rail services for commuters.
What are Off-Peak Hours?
Off-peak hours refer to the non-peak periods of public transportation usage.
During these hours, the demand for transportation is typically lower, and commuters may enjoy lower fares or less crowded train systems.
What is the SMRT Light Rail?
The SMRT Light Rail refers to the light rail systems operated by SMRT Corporation Ltd in Singapore.
It includes the Bukit Panjang LRT system, which provides additional connectivity to the Bukit Panjang area.